Since first emerging in 1992 the term “blog” has come a long way and become one of the largest segments of the Internet. It made expressing and sharing thoughts accessible to everyone. The explosive growth of social networks changed the game though, killing off diaries and livejournals, as well as essentially merging both terms – social networks and blogging.
Today the right combination of audience engagement and content quality allows to leverage a blog making it a tool for corporate PR campaigns and/or a source of income for individual bloggers. In this guide we set the goal of covering all the aspects of how to start a blog, albeit in its conventional web page format. Blog hosting, CMS, setting up, posting, publishing, promoting, monetization, along with tips, pitfalls, do’s and don’ts to get things going.
Preparation stage: Blog hosting services
Facebook, Instagram, YouTube, Tik Tok, etc. is one thing, but for an old-school blog one needs to get a web hosting first. In general, there are 3 hosting options: own setup, blogging platforms and standalone host.
- Own hosting setup
Pros: free, full control
Cons: requires special skills, home network prone to threats
To start a blog and deploy it on your own computer, you have to download and install a suitable server engine – to process incoming requests. Then you have to install a database (compatible with the engine) to make content available to visitors. Then, an access hierarchy to set the admin rights and to prevent visitors from editing content. Also, an Internet provider with an appropriate bandwidth and powerful hardware.
Of course, this is only a general overview, and for each step there are tons of instructions online to go through for home hosting. We don’t recommend this option as an incorrectly configured home server could put blog content and all devices within the network under great risk of malicious actions by hackers.
- Hosting on web platforms
Pros: convenience, technical support
Cons: partial control over content, no full access to code
When you start a blog merely to share thoughts and experiences, web/blog platforms like WordPress, Blogger, Wix, etc. are just fine. The advantage is that the technical side is taken care of – you just make the creative choices, e.g. domain name, theme, design, posting. Online blogging platforms can be divided into three groups:
Universal web platforms. Also might be referred to as “website builders” with a layout adapted for blogs. Famous examples are Wix and WordPress. These are visual builders with a CMS (content management system), media, plugin integration options, tools for payments, etc.
Pros
Cons
Classic blogging platforms. Low learning curve due to basic functionality, which, on the other hand, limits the possibility to give a blog a unique face. A top example is Blogger, one of the oldest online blogger platforms by Google. The latter fact makes for many perks: authorization via Google account, AdSense, RSS feed.
Pros
- Fast, easy to use
- Compatible with many devices
Cons
- Basic functionality
- No custom code integration
Hybrid platforms. Basically a result of digital evolution, blending blogging and social media elements together. A nice example would be Medium, where articles are posted by users and discussed by readers. Readers can like and comment posts, follow favorite authors and share links to articles. The downside is inability to customize pages to one’s liking.

The main advantage is time to get content published – typically, it takes about 5 minutes to launch a blog there, and then posting is instant. However, moderators can remove posts or block accounts entirely if they deem content inappropriate.
Pros
- Huge audience
- Instant posting
- Social interaction
Cons
- Moderated content
- Many features must be purchased
- Standalone hosting
Pros: full access to content and source code editing
Cons: expensive
Optimal though largely depends on the host’s terms of service. Ideally, the hosting company should provide: good bandwidth, protection against hacking, malware, ransomware; tools for CMS deployment, backups, full access to the root folder.
Some hosting companies provide assistance with site migration, domain name purchase, email setup, SSL certificate, etc. Yet each of these gigs will increase the final price of hosting. In my view, the most critical part is backups (at least manually), SSL certificate support and two-factor authentication to the server control panel.
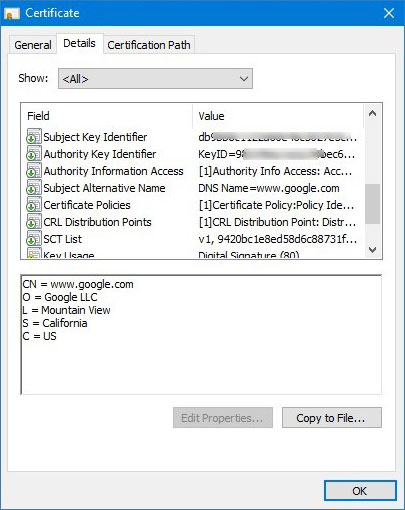
SSL certificate is a special file defining conditions for encrypting traffic between visitors and a web site. It provides protection against interception of traffic, and its presence is one of the key conditions for appearing in search engine results.
We’ve analyzed offers from the 10 most popular hosting companies and summed their basic plans in this table:
| Hosting | Plan | Price for year | Storage | SSL | Backups | 2FA |
| A2 Hosting | Startup | $84 | 100 GB | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| BlueHost | Basic | $72 | 50 GB | $40 extra | $36 extra | Yes |
| GoDaddy | Basic | $48 | 100 GB | $60 extra | $24 extra | Yes |
| GreenGeeks | Lite | $30 | Unlimited | Free | Yes | Yes |
| HealthInternet | Economy | $48 | 100 GB | $50 extra | Yes (manual) | Yes |
| HostGator | Hatchling | $33 | Unlimited | Yes | $24 extra | No |
| Hostinger | Single Shared | $36 | 10 GB | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| InMotion | Lauch | $84 | 50 GB | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Kinsta | Starter | $360 | 10 GB | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Siteground | Startup | $84 | 10 GB | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Also,all hosting companies have such an option as renewal – the cost of prolonging hosting after subscription expires. Some providers set renewal prices higher than initial subscription, therefore please take it seriously when choosing a hosting provider.
How to come up with a blog name
Here are several tips for naming a blog based on top culinary blog examples by ChefsPencil, where competition is fierce, and thus creativity reigns.
- Don’t use generic words – “Blog about cooking”, “Culinary blog” etc.
- Check if domain name is free, as the same-sounding domain as the blog title is important.
- Try to stick closer to the topic. Example: off two new culinary blogs called Smitten Kitchen and Balanced Bites readers will more probably choose the first one.
- If domain name is taken, but the concept is strong, tweak it slightly. Food52 added numbers and The Kitchn removed one letter, which didn’t affect the perception, but made the exclusive name.
- If you own a well-known brand, why not use it?
- Add topical words to create engaging titles like Minimalist Baker or Simply Recipes.
- If not planning to sell the blog in the future, use your own name in its title, just like Cookie and Kate and Sally’s Baking Addiction did.
The name should be associated with the blog’s content and be unique. Ideally, it should also be easy for typing.
Selecting a domain name
Again, in most cases it is the same as the blog title, although not a rule. Separation into levels is by dots in the name, for example, Thinkmobiles.com is located at the top (first) domain level – com. In other words, if the name one has in mind (myblog.com) is already taken, it is better to try finding another top-level domain, i.e. myblog.net, myblog.de.
When using a free domain, say by Blogger, the address will be – title.blogger.com. Lower level domains, as a rule, are cheaper but are at risk of being discontinued, for instance if Blogger.com is closed or apprehended by hackers. At this point, many novices are still confused about hosting and domain differences, so here’s one analogy that may help:
- Domain name (title.blogger.com) = house address (Madison street 15)
- Hosting (server for content) = house itself as a physical object
- Blog (content) = house residents living in the building
Overall, the shorter and more concise, the easier it is to remember. For example, The New York Times goes with nytimes.com, which is definitely better than thenewyorktimes.com, and more recognizable than just nyt.com.
One can purchase a domain from domain registrars, as well as hosting providers often offering it as an additional service. I’d recommend the latter option, because then domain and hosting can be managed from the same admin panel.
A little research shows that buying a domain name from another registrar can save up to $20 per year. Here is a comparison of prices from different domain registrars:
| Domain | Google Domains | NameCheap | GoDaddy | Domain.com | Bluehost | Hostinger |
| .com | $12 | $9 | $12 | $10 | $13 | $9 |
| .net | $12 | $10 | $15 | $13 | $15 | $13 |
| .org | $12 | $8 | $10 | $9 | $10 | $12 |
| .site | $20 | $2 | $1 | $5 | $3 | $1 |
| .co | $30 | $4 | $12 | $11 | $15 | $24 |
| .me | $20 | $3 | $8 | $3 | $12 | $7 |
| .us | $12 | $4 | $20 | $5 | $18 | $9 |
| .info | $12 | $4 | $3 | $4 | $12 | $4 |
| .eu | N/A | $5 | $13 | N/A | N/A | $7 |
| .blog | $30 | $7 | $10 | $7 | $23 | N/A |
There are also cheaper domains, such as .xyz, .site, .tech, etc., however they look less respectable, and moreover, are often used by hackers and thus people tend to avoid such websites.
There are domains that can be purchased only when meeting certain conditions. For example, only companies registered in the European Union can use the .eu domain, and similarly the .us domain is only for US citizens or companies.
Selecting blog engine / CMS
You’ll see both terms online – blog engine and CMS (content management system), that practically mean the same thing. Herein, engine is the core functionality for publishing and editing articles. Adding additional modules to it turns it into a CMS, and there’s no way around it.
CMS is a collection of modules for blog lifecycle. Without diving into technical intricacies, we can say that the most popular are WordPress, Joomla and Drupal. WordPress takes up more than a half of all web sites as of January 2021, according to research by W3Tech.
In general, CMS allows you to manage a blog and its content via a visual interface and without the need of coding. Now, the list of modules typical for CMS:
| Module / Subsystem | Importance | Description |
| Articles editor | Necessary | Creating and editing article content |
| Articles manager | Necessary | Managing (deleting, hiding) published articles |
| Login system | Necessary | Control access to the admin panel and editing tools |
| Media files manager | Recommended | Manage uploaded photo, video, audio files |
| Style manager | Recommended | Setting a single display style for all blog pages (menu, footer) |
| Pages editor | Recommended | Management of technical pages |
| User rights management | Recommended | Creating additional access levels besides administrator, moderators and readers |
| Export / Import system | Recommended | Creating / restoring backups |
| Status bar | Optional | Mainpage for the administrator displaying issues that demand attention |
| Designation / identifier system | Optional | Tags, categories, subcategories |
| Plugin manager | Optional | Adding and managing plugins / addons |
To start a blog with CMS (WordPress for example), one has to download it from the official site and unpack it to the root folder on the server. Then initialize the database and associate it with the blog – a username with a password and the database name are required. Most hosting providers automate all these steps, e.g. WordPress via 1-click install tool.
NB. Do not use the same credentials for CMS and hosting admin panels. Hosting administrator accounts are usually well protected and use additional authentication methods, while unauthorized access to the CMS can be obtained by exploiting zero-day vulnerability. If a hosting provider doesn’t have the option to quickly activate CMS, study step-by-step tutorials for WordPress, Drupal or Joomla.
How to install WordPress (guide)
This guide is meant to help install WordPress on a new (empty) hosting service where no 1-click installer is provided.
1. Download the archive with WordPress files from the official web site.
2. Clear the root folder of your hosting from the default files and folders to avoid conflicts. Then unpack the archive to the server’s root folder. After correct unpacking, files and folders with the wp- prefix should appear in the blog folder.
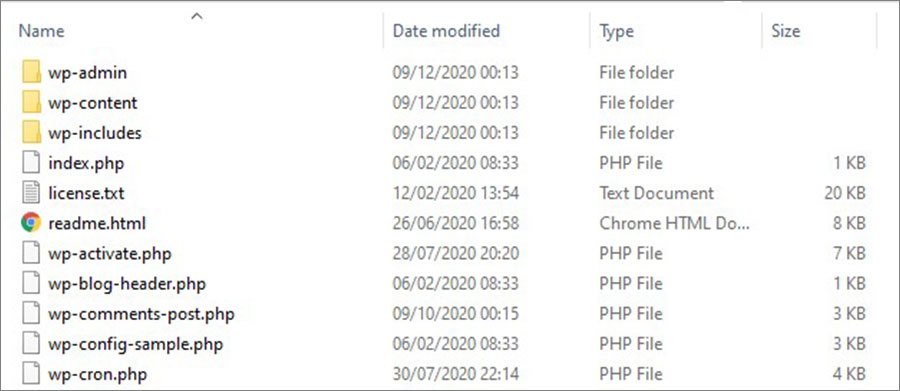
The root folder is the highest folder in the file manager hierarchy. Usually, for new projects it opens by default, but if it doesn’t, go to file manager and click Up until reaching the desired level.
3. Open the blog in a browser. Instead of a blank page, you should now be prompted to start installing WordPress. Click Let’s go.
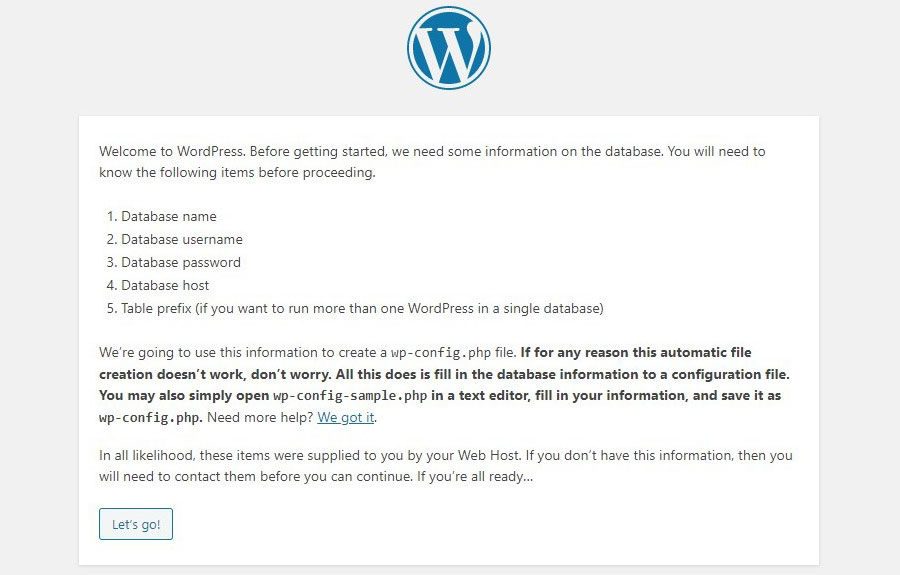
Don’t leave this stage unattended as there is no user management so far, thus any unauthorized persons could try to complete the installation. If there’s no welcoming screen, clear the root folder and unpack the CMS again.
4. In WordPress, all basic information is stored in a database which must be configured too. Open a new browser tab and go to the DB manager. Create a new DB user with rights to create, read and write values to the database. The link to database management is usually located in the hosting admin panel.
5. In the general list of tables, create a new database and give it a name.
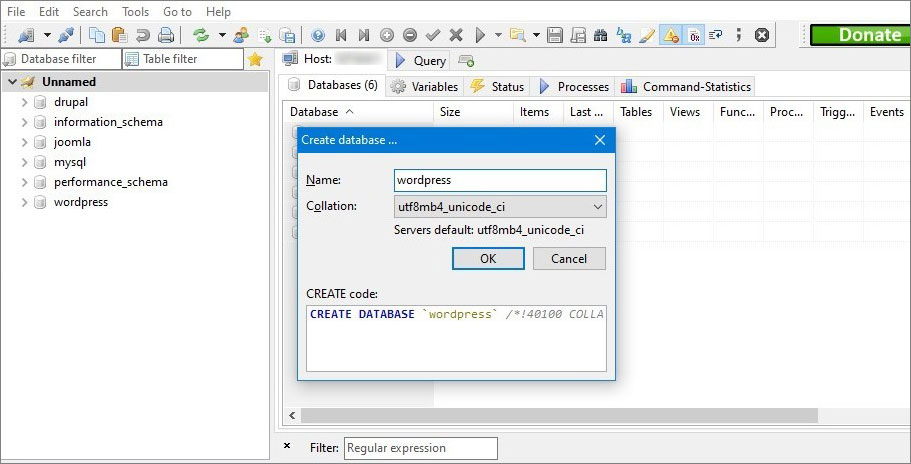
6. Enter in the appropriate fields: DB name, username, password and click Submit.
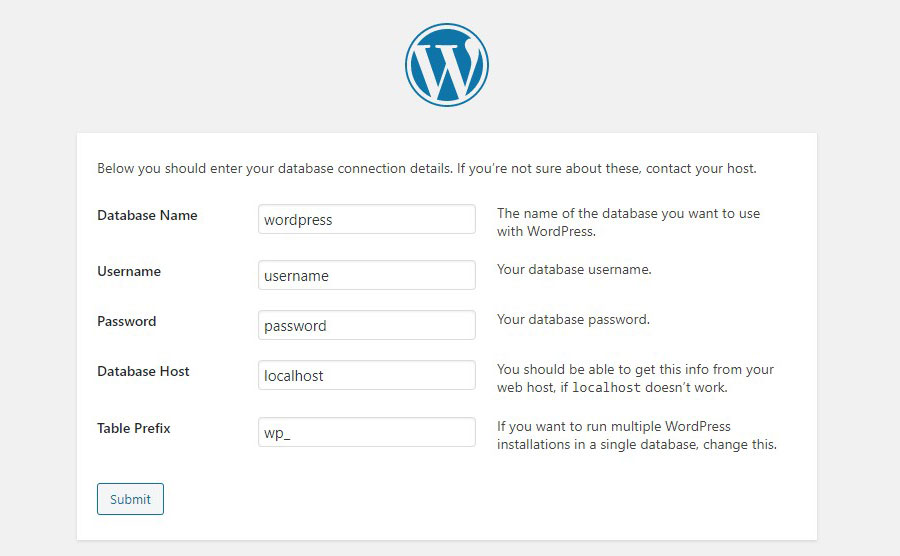
7. Click Run the installation in the next window. If it’s not available, then you made a mistake when specifying data to connect to the database. Read the error message and return to the previous step to fix it.
8. Fill in the following identification data: site title, username, password, email (we recommend registering a new separate email), search engine visibility checkbox. Then click Install WordPress and then log in.
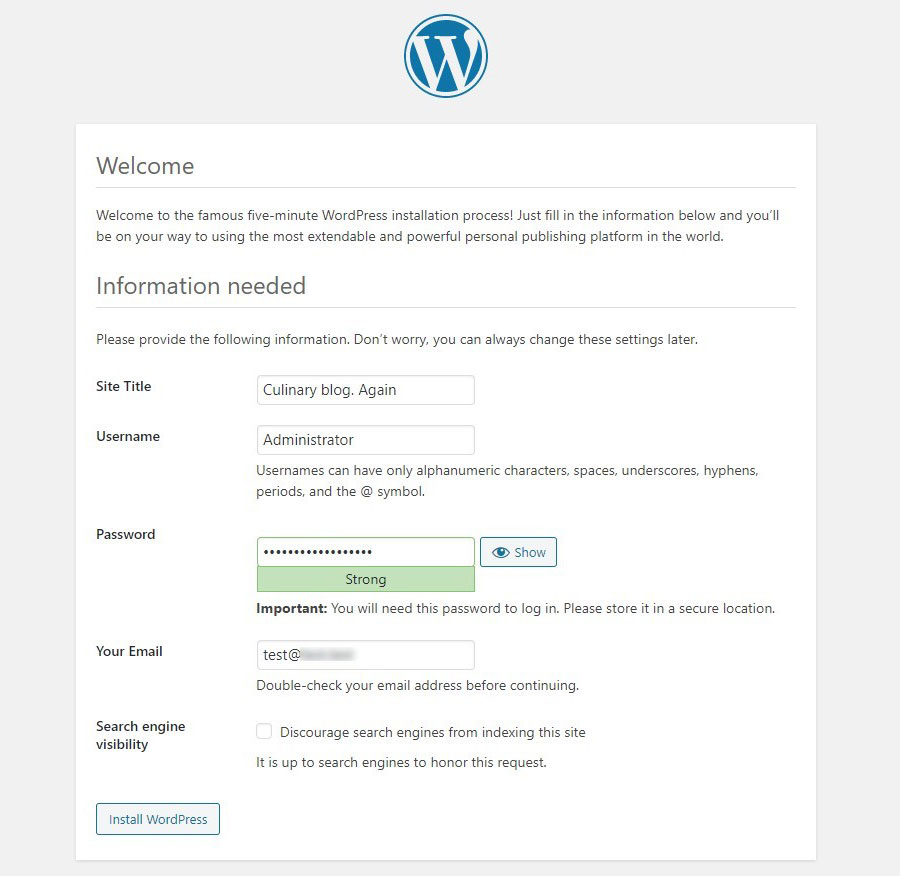
How to install Drupal (guide)
- Download Drupal from the official site and, using the file manager, unpack the contents to the root folder of your blog.
- Open the site, select the installation language.
- Select the Standard installation profile and proceed.
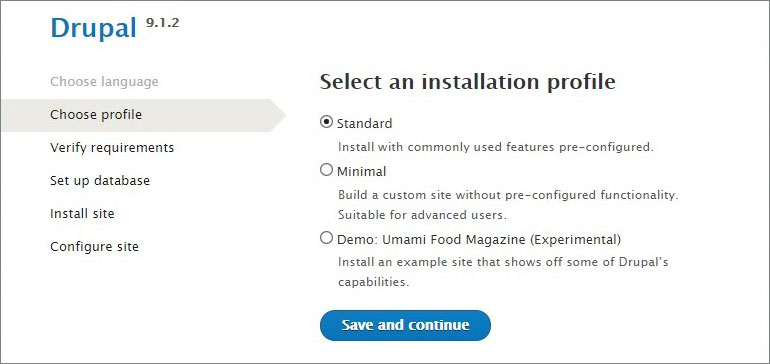
- Create a new database and a user with access to it in the database management software. Then click Save and continue. If all is correct Drupal will start installing its files and records in the database. Wait until complete.
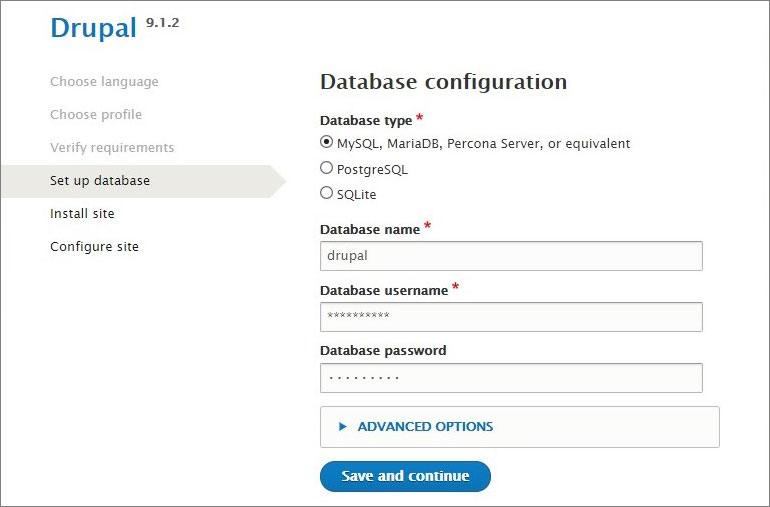
- Fill the identification information. Note that in Drupal (unlike WordPress) you can set different emails for administrator accounts and public connection.
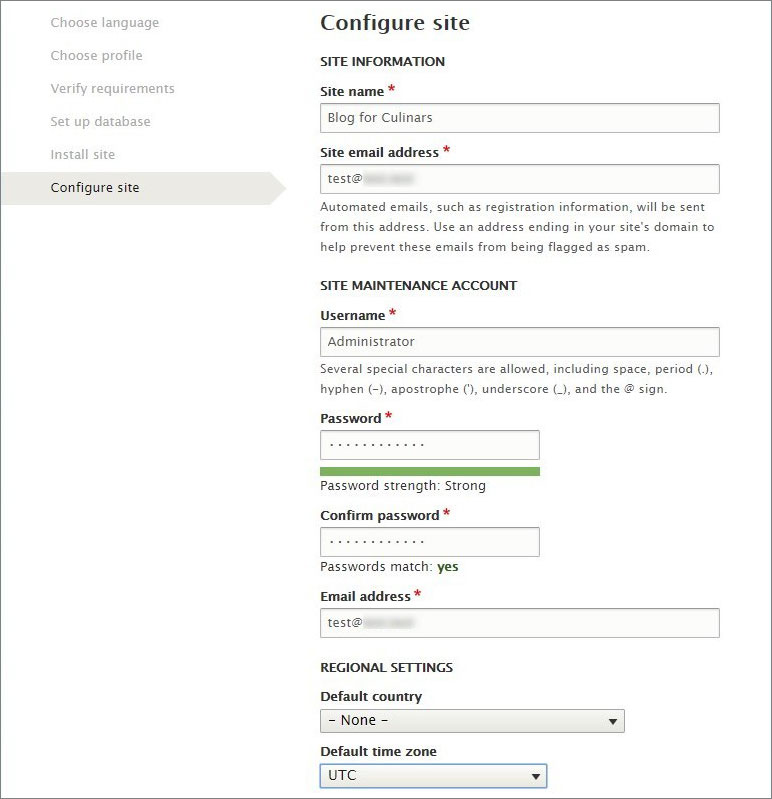
If the blog has a local nature, don’t forget to specify time zone and location in Regional settings. If it is global, use the UTC time zone.
How to install Joomla (guide)
- Unpack the archive to the root folder.
- Enter the blog name and a small description (optional). Then fill in the details for the blog admin account. It would be better to use separate email for this account.
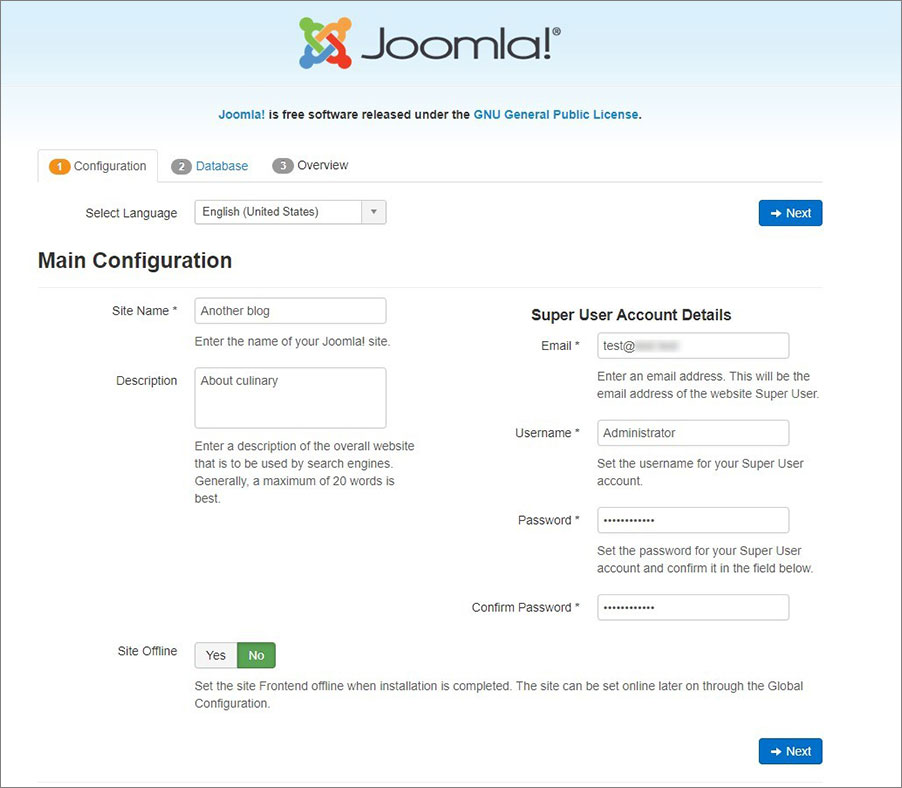
On this page, Joomla has the Site Offline feature making the site unavailable publicly until it’s not fully set up. We recommend enabling it.
- Create the user and a new database for Joomla using the database manager. Use this data for the Database Configuration window.
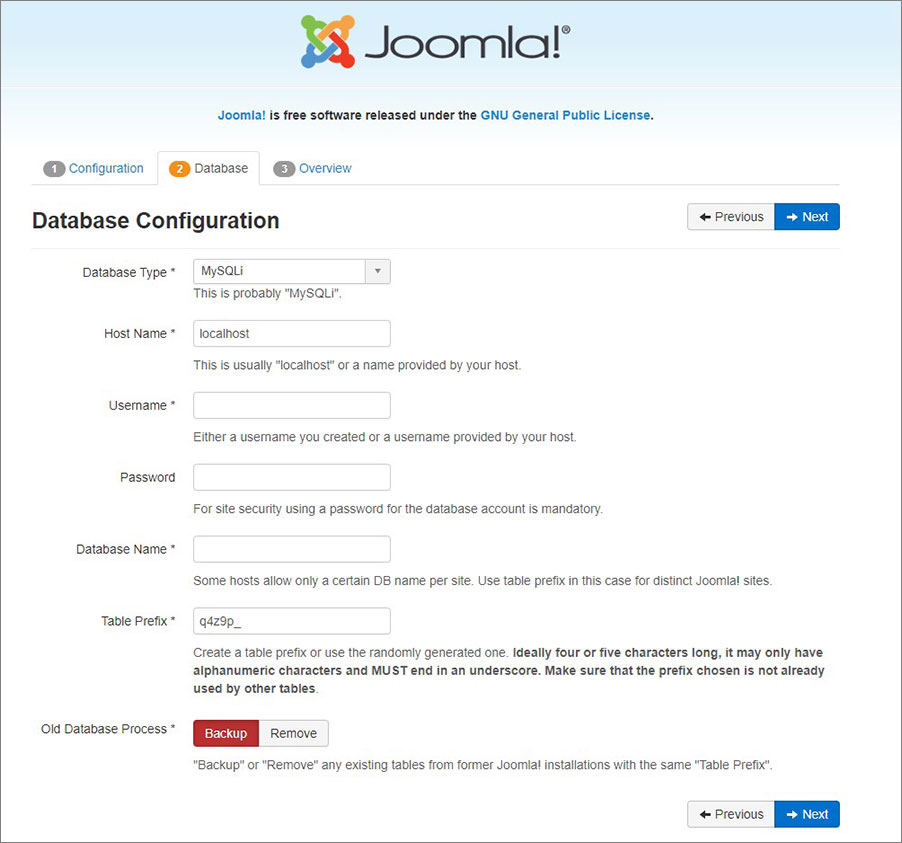
- On the Finalization stage, select Blog in the Install Sample Data section if you want to add article samples to storage. Click Install and wait until finished.
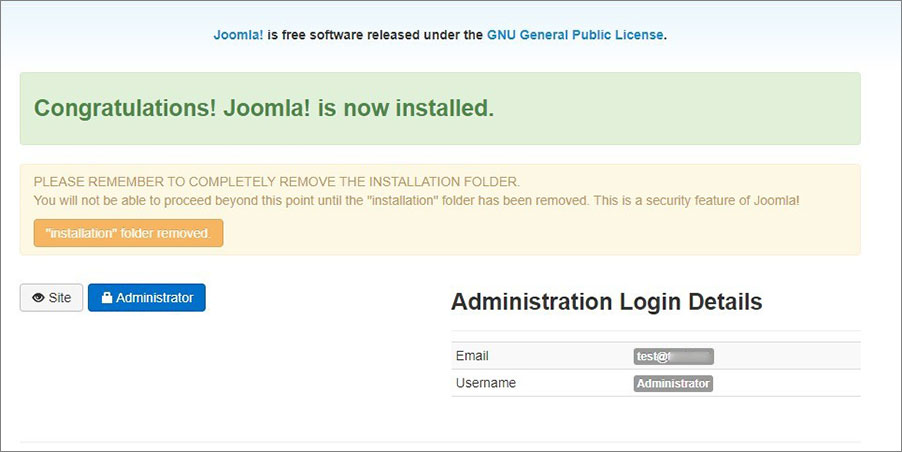
- Click Remove installation folder to complete the installation.
Publishing stage: Blog types
Think of content type after the technical setup, or vice versa, it’s up to you. I prefer learning about all the capabilities of a chosen CMS first and then determining the blog format. Developing your own style would be very helpful in terms of user recognition. For example, for a personal blog the first person (I) views are appropriate, while a news blog would state facts in a passive voice (something happened). Just a small example.
We can distinguish 6 main types of blogs:
- Personal diary
The one that everyone is familiar with. Despite the sharp drop in popularity due to the appearance of social media, it is still used by many to mark life events, share experiences, or just honing writing skills. Monetization is poor.
- News aggregator
Important to determine the direction and post subjects in advance: technology, politics, healthcare, etc. Usually presented in a neutral form, without personal judgments. Monetization options depend on the target audience. For example, global news have larger audiences, yet niche blog followers are more active in terms of donations and subscriptions.
- Professional blog
More likely to make profits, as authors use it to showcase their expertise in certain areas as well as a point of interaction with potential customers. Materials should always be informative and useful to readers.
- Hobby blog
Similar to professional blogs in terms of one-area focus, but less strict. As a rule, there’s an active community around a theme: comic books, music, hiking, tourism, etc. On the other hand, monetization is less probable, and most often it is just voluntary donations to keep it afloat.
- Showcase
The most prospective blog type for monetization and here’s why. The content usually involves reviews, comparative ratings of products, services, places, events in various fields, thus invoking interest from businesses and corporations. Once a blog amasses a strong reputation and following, it becomes a force to be reckoned with. Advertising requests come in droves.
- Thematic content blog
Authors can publish exclusively or allow user-generated content from trusted people. Think of Buzzfeed or Medium. Contents may contain media files (audio, video, pictures). Often used to promote goods or merchandise in a light entertaining manner.
Blog post (content) types
The basis of any site is content, in the case of blogs we are talking about posts. This stage traditionally causes trouble, because novice bloggers can’t find sources of information and choose fascinating topics to start a blog. We have compiled a list of 10 most promising content types that could hopefully enlighten one’s path.
-
Expert opinions
For niche blogs experts of the field/industry are welcome. Even if you yourself are an expert, inviting other people shows openness. Better than a comment from an expert would be a full interview. Podcasts are on a sharp rise, bare in mind, both audio and video. The easiest way for beginners in blogging is to invite experts to refute or confirm popular questions from a given area.
Examples: Expert opinion, Interview, Myths and popular questions.
-
Personal
Sharing author’s personal life and events. Be careful not to share personal information though: ID, address, family, etc. Emotional content resonates most with followers. Famous people and experts gather larger following around their active profiles. Topics could be tips for solving problems, business startup story, weight loss, personal development, film reviews, etc.
Examples: Private diary, Advices, Personal experience.
-
Tutorials, guides, tips
These posts require extensive and scrupulous preliminary research. First of all the author must find common problems, and then lay out solutions in the form of a step-by-step guide. Each step of a guide should be written with the assumption that previous steps were finished successfully. One form of guides could be case studies, that, from a marketing point of view, have good advertising value.
Examples: Guides, Case Studies, Glossary, Tutorial.
-
Lists
The biggest share of evergreen content belongs to lists. Evergreen is the type of content which, if written correctly, remains relevant for a long time. Best science-fiction books to read in 2021, must-visit restaurants in Nice, a checklist before going long-distance hiking, lists with cheat sheets – sky’s the limit, as they say.
Examples: List, Checklist, Cheatsheet.
-
Interactive posts
To increase user engagement bloggers often offer rewards for certain actions, sometimes timed to holidays (Christmas) or linked to blog achievements (10K subscribers). To track posts, you can ask followers to use hashtags, as Facebook, Twitter, Instagram can track it then. Polls, surveys, giveaways are among popular options.
Examples: Surveys, Quizzes, Free Giveaway.
-
Opinions
To post your views on things or let others do it with argumentation. Say, you’re a sports fan, so you may comment on favorite kind of sports, games, clubs, news, etc., criticize or praise, ask readers what they think, invite guests to comment or guest posts to react to certain events. Motivational and inspirational posts are also quite popular, showcasing success stories by reputable people.
Examples: Open letter, Thankful post, Debates.
-
Entertainment
Grabbing audience attention the most and holding it until a trend dies down. Many visitors are guaranteed to stay as regular readers. Content may be frivolous and loose, humorous and ironic, and even gossipy, whatever you like.
Examples: Funny texts, Funny images, Funny videos.
-
Events and news
These posts should be frequent to stay relevant, as there are tons of things happening all the time. There are hundreds of content sources too: from official political press releases to social media accounts. In practice, it’s hard to maintain a blog with a large number of different categories of news. Therefore, sticking to one or two categories is recommended.
Examples: News, Event and holidays, Topical selection.
-
Answers
Millions of people google questions every day. For the most part, they search what is best and what is free, as well as how to do the X thing. Naturally, pages with answers are in high demand. It is important to create titles and descriptions that best match search queries. Detailed answers, explanations, tips and links to authoritative sources are must too. One form is FAQ from vendors of products or services. Video tutorials are going strong as well.
Examples: FAQ, Recipes, Solutions.
-
Reviews
Today there is an opportunity to leave a review about everything: places (TripAdvisor), hotels (Booking), products (Amazon). But detailed and expert reviews that offer more than just “good” or “bad” from user ratings are sought after. Personal experience is a significant factor. In general, any review should include a description of all moments of interaction with the subject of the review, its best aspects and user tips. Review a single thing, compare several similar products, or compile best-lists, it’s up to you.
Examples: Comparison, User experience, Bests of something.
Planning content strategy ahead, with posts, dates, drafts, user metrics, etc., could help tackle creative crises along the way. Over time, you will definitely build the audience and find the right type of posts and style.
How to publish posts in WordPress (manual)
- Open your blog page (myblog.com). Add /admin to the address bar to get to the login form.
- Enter the administrator login and password for WordPress.
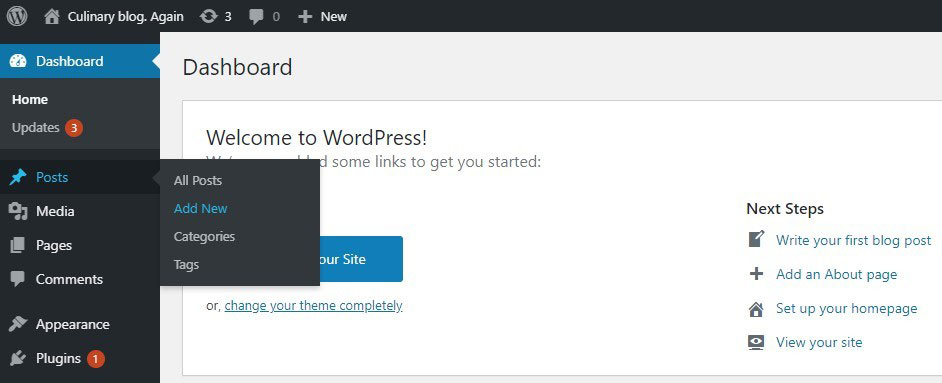
- Select Posts – Add New to open the post editor.
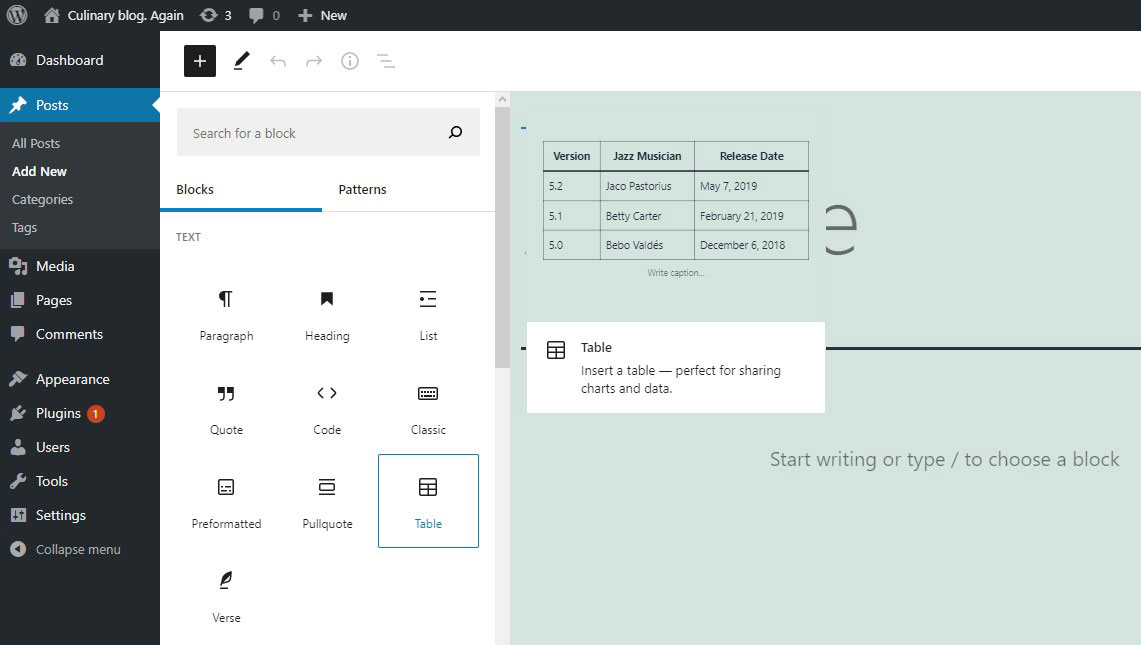
- Add the article content – title, body, pictures. Click Publish.
- To edit or update posts after publishing, find a post and click Edit next to it.
How to publish posts in Drupal (manual)
- Open your blog page and log into your admin account. If there is the My account button on the top right, you are already logged in.
- On the top bar, click Manage – Content to open to the article management menu.
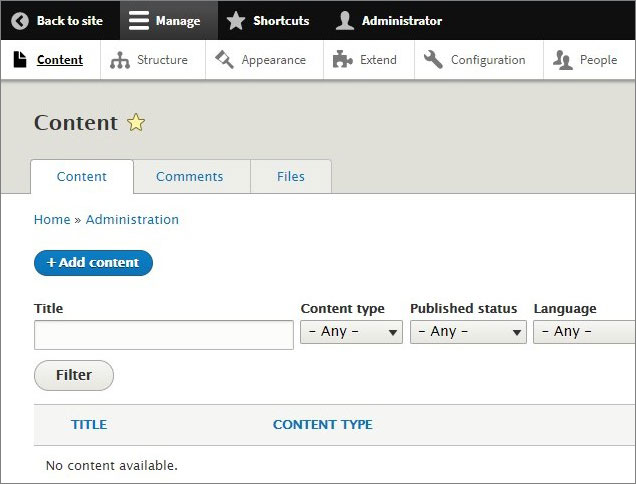
- In the next window click Add content and Article to open the post editor.
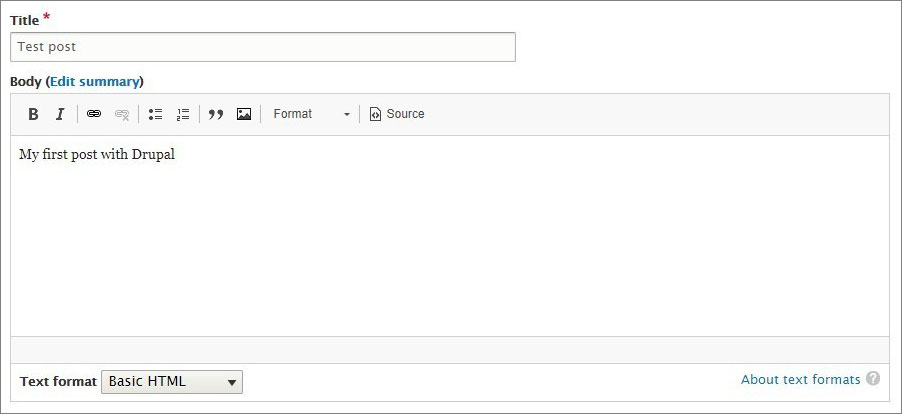
- Set your post title to Title. Then add all the text to the body field and format it using the elements in the editing panel.
- Add article tags and a cover image. If you don’t know what it is, leave these fields empty for now.
- Tick the Published field and click Preview to preview or Save to publish. Drupal has a simpler and more traditional post editor than WordPress, however, with slightly limited features.
How to publish posts in Joomla (manual)
- Open your blog in a browser and log in using the admin keys generated during setup.
- Click Site Administrator and log in again to access the admin panel. Joomla has separate authorizations for front-end (visible part of the blog) and back-end (admin panel).
- Click New Article from the list of features.
- Add the title, text, format all with the editor.
- Set the post category to Blog and check the settings for other post properties in the panel on the right.
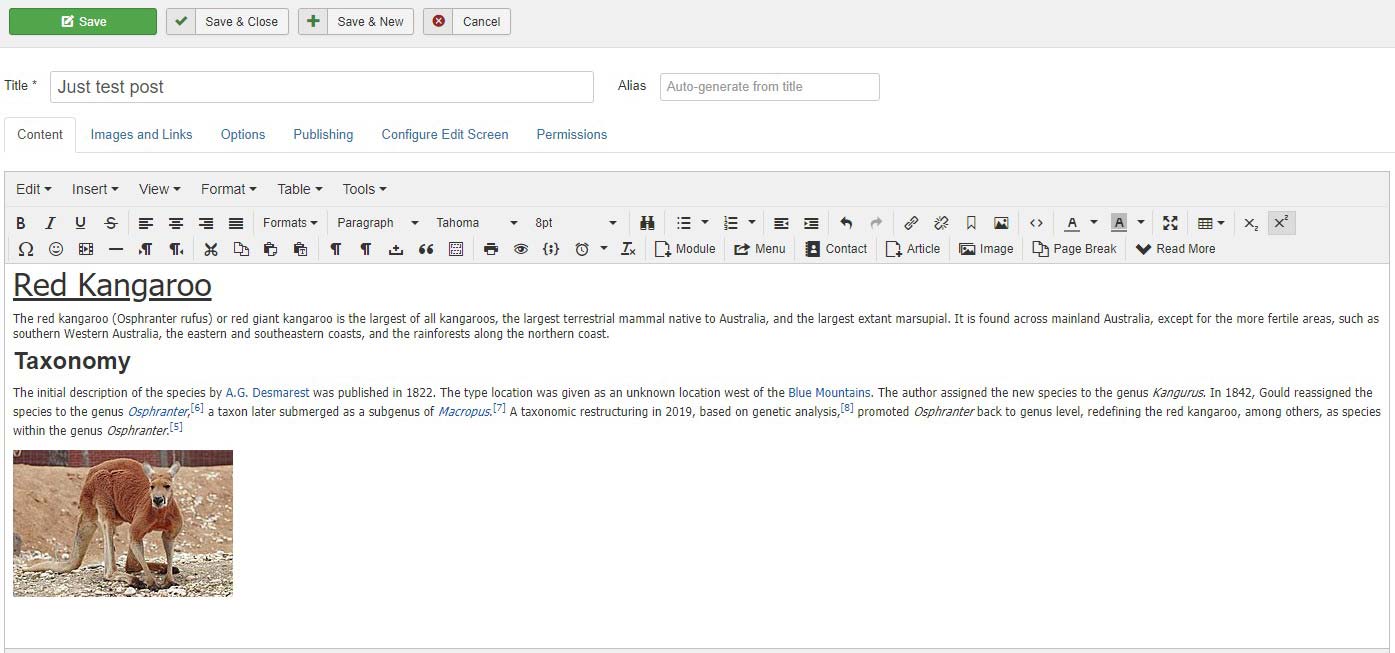
- Click Save to publish the post.
Blogging stage: Analytics, monetization, maintenance
One of the challenges of blogging is inability to accurately predict audience reactions and growth of a project. Collecting data on user behavior and engagement is of high value. Blog owners can apply a variety of analytical tools: Google Analytics, third-party plugins (MonsterInsights), custom apps.
Google Analytics is supported by most modern CMS, it is free and relatively easy to integrate. Without affecting page load speed, it collects such data as number of visits, user devices/platform, location/country, time spent on pages, etc.
NB: Most countries’ legislature requires websites and blogs to have the Privacy Policy section explaining what information is being collected and ways it is utilized.
- How to set up Google Analytics
- On the Google Analytics page, log in with the Google account and click Start for free (or Sign in if you already have an account).
- Enter your blog name in the Account name field. Tick sharing information with Google products & services, other fields are optional, but we recommend having them enabled too.
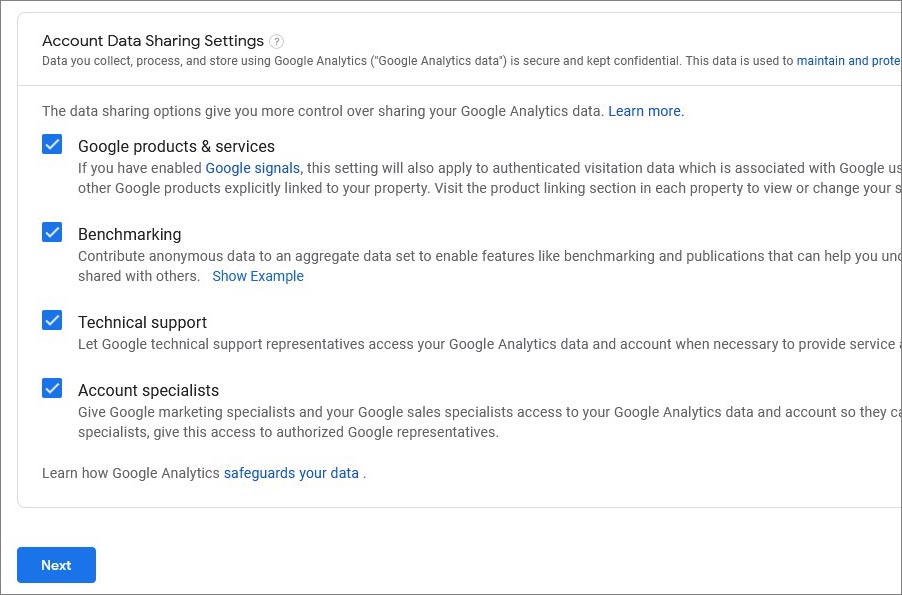
- In the Property setup, set the time zone and currency.
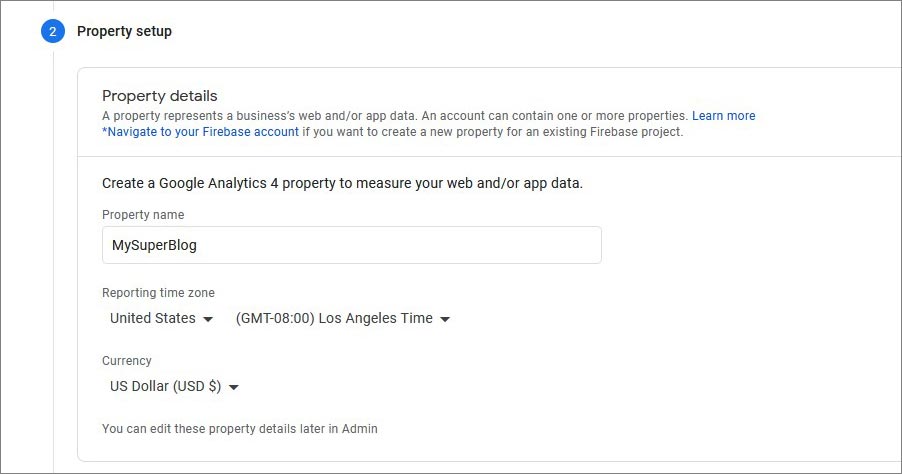
- Answer the required questions in the About section. Read and accept the Privacy Policy. Choose what notifications to receive by email.
- Choose a web platform and create the Stream for your blog. To do this, enter the site address and name the stream.
- Return to dashboard, go to Admin – Setup Assistant – Data Streams -Tag installation and select Web platform. Click on the name and select the Global site tag. Copy the provided code snippet.
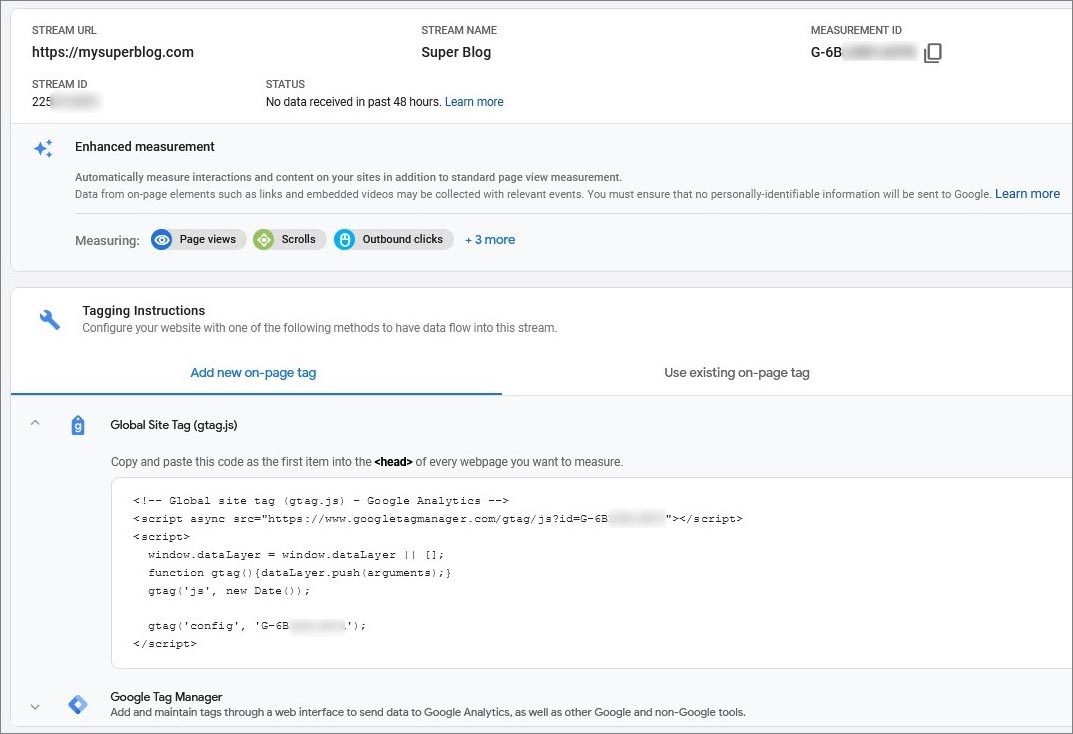
- Paste this code or ID into the structure of blog pages. Use the official manual about Google Analytics integration to websites.
- In WordPress, add the copied code to the header.php file in the root folder.
- In Joomla, go to the Extensions – Templates – Templates in the admin panel and add the code to all templates.
- In Drupal, use the special GA integration extension.
Blog monetization options
Earning money from blogging, a.k.a. monetization, has been attracting interest due to the rise of bloggers, podcasters and entertainers in recent years. High-quality content is bringing large audiences. There are 4 main types of potential income from blogs:
- Donations
When followers voluntarily transfer money to support the author, one-time or recurring. The main rule – do not spend these funds on things other than declared purpose. It is good practice to regularly publish bills that were paid via raised funds. We recommend using plugins for payments only from official stores for the CMS or by your bank (as an API).
- Subscription
A more stable source of income that allows better planning of future expenses. Unlike regular donations, a subscription necessarily provides exclusive content or services.
- Affiliate partnership
Expressed in booked campaigns to increase sales by other brands through advertising on your site. They can pay for clicks, registrations, purchases, etc.
- Direct sales
Modern CMSs (WordPress) make it possible to deploy basic e-shop. One can boost the demand for products by publishing relevant posts. On the other hand, it may be difficult to pull off. A blog must have certain recognition in order to attract paying visitors.
Blog maintenance
In short, regular blog maintenance is sensible. Few rules of thumb next. Check and install CMS updates – it will add more features and fix vulnerabilities. Before updates, be sure to make a backup at least for the content. From time to time revisit published posts to see if titles, pictures and other details are relevant.
Check links to external sources, especially videos. If you have communication channels with users, attend to it as often as possible, be it emails, comments, etc. Create a publicly accessible Terms of Services page with rules of user behavior and possible penalties. ToS and Privacy Policy pages should contain the last update date.
How to start a blog: Conclusion
Two most difficult moments are initial setup and first publication. Further actions may be different: for a hobby blog 2-3 hours a day will do, while the “real deal” profile aiming at earning will require much more time and effort. To start a blog, you need to know the basics of the digital environment, the Internet, software, payments, etc.
As a blog grows, you can delegate some tasks to trusted people. Creating posts is inherently creative work, but the more experience you collect, the easier it will become to create and edit. Try to maintain one style for all posts, stories, videos, podcasts, yet do not be afraid to experiment from time to time to diversify and break the stale when it happens.
Read next: Blog ideas to get you started.

